About X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM)
|
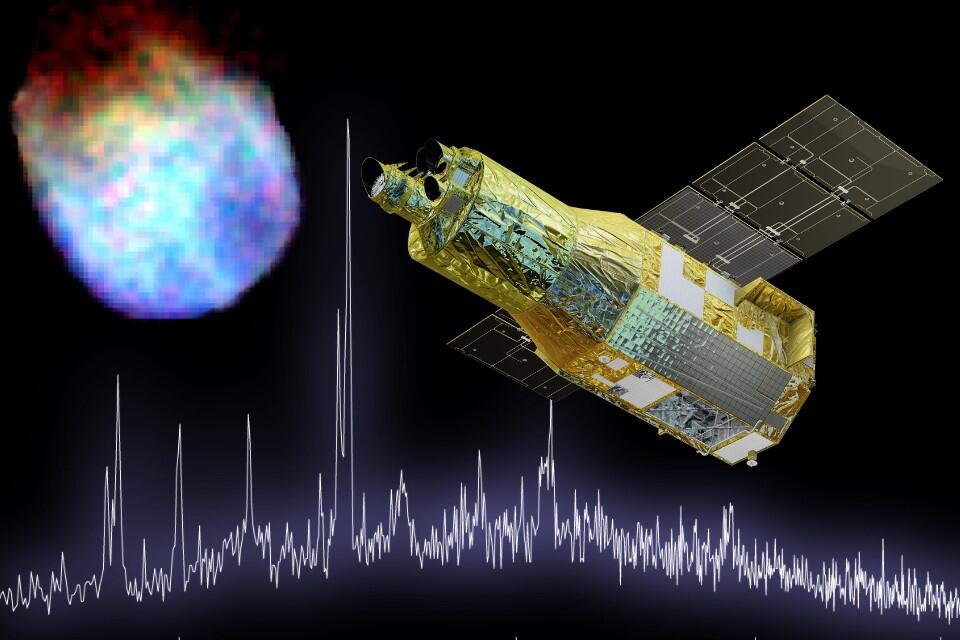
XRISM is installed with the latest X-ray spectrometer and X-ray imager, which are used to observe |
|---|
Project Topics
indexLive Coverage: Launch of the X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM) and the Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) onboard the H-IIA Launch Vehicle No. 47 [Rescheduled]
|
JAXA will provide the live coverage of the launch of the X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM) and the Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) onboard the H-IIA Launch Vehicle No. 47 (H-IIA F47). Broadcast Time: around 8:10 a.m. to 9:40 a.m. (JST) on September 7, 2023/ 23:10 p.m. on September 6 to 0:40 a.m. (UTC) on September 7, 2023 Launch Time: 8:42:11 A.M. (JST) on September 7, 2023 / 23:42:11 p.m. (UTC) on September 6, 2023 Launch Site: Launch Site: JAXA Tanegas... |
Press Release
index-
- Feb. 13, 2025 (10:00) [release]
- Study Based on Observation Data from X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM) Published in Nature
Characteristics of X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM)
Scientific Enigmas for XRISM to Investigate
By measuring the velocity and makeup of the plasma between stars and galaxies, XRISM will resolve more precisely than ever how these celestial objects are formed.
Spectroscopy and Imaging of XRISM
Spectroscopy is the measuring of the strength of light at different wavelengths, in the same way our eyes can see different shades of colors. In X-ray astronomy, by making a precise measurement of wavelength (energy) of X-ray photons in the universe, we can measure the temperature of celestial objects, the type of matter they contain, and their speed. The micro-calorimeter, Resolve, has excellent spectroscopic capabilities. On the other hand, imaging takes a picture of an object. By examining the shape and brightness distribution, we can learn about the spatial extent of celestial objects. XRISM has an X-ray CCD camera, Xtend, which can image objects over a wide field of view.
Major Characteristics
| Name | XRISM (X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission) |
|---|---|
| Weight | 2.3 t |
| Orbital Altitude | 550 +/- 50 km |
| Orbital Inclinarion | 31 degree |
| Mission instruments (Planned) | Resolve (Soft X-ray Spectrometer) / Xtend (Soft X-ray Imager) |