Research and Development Directorate
Ensuring the Safety of Spacecraft Flying in Low Earth Orbits
Developing the International Standard
for the Use of AO Protective Technology for
Low Earth Orbit Spacecraft
Spacecraft such as the International Space Station (ISS) and satellites are orbiting at altitudes of about several hundred kilometers, and there exists a lot of atomic oxygen (AO) at such low orbit altitudes. AO is formed when oxygen molecules are photo-dissociated by ultraviolet radiation from the sun. AO is notorious as a factor that lowers the performance of plastic materials used on the outer surface of spacecraft by hitting the surface and degrading the materials.
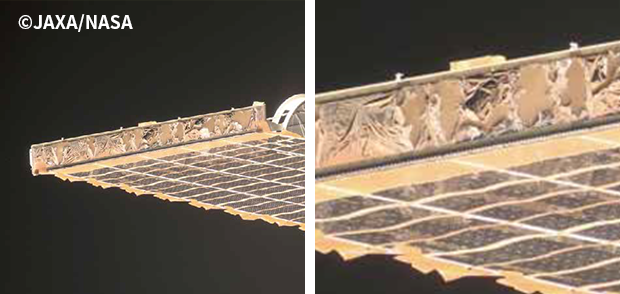
The Research and Development Directorate has long been conducting research to develop technology to assess the impact of AO on materials used for spacecraft and measures to mitigate the impact, such as coating the materials. In this effort, the Directorate also implemented technological demonstration projects by utilizing the H-II Transfer Vehicle “KOUNOTORI” used to resupply the ISS and the Super Low Altitude Test Satellite “TSUBAME.”
Based on the achievements made through the aforementioned initiatives, JAXA proposed the setting of an international standard for atomic oxygen protective coatings on polyimide film in 2017. Then, following about four-year discussions and voting by experts from each country, ISO 23129 was published as the international standard for the coatings in September 2021. In ISO 23129, silsesquioxane (SQ) coating, which JAXA developed jointly with a company in the private sector is included as a type of AO protective coatings usable for spacecraft.
KIMOTO Yugo, Research Unit I of the Research and Development Directorate, has been leading the research and proposal for the international standard. He says, “Space activities in low earth orbits have been promoted globally, and it is urgently necessary to implement measures against AO. The international standard for AO protective coatings shows the selection criteria for the coating materials, thereby contributing to establishing the infrastructure necessary to promote low earth orbit activities including those conducted by the industrial circles.”
Anti-AO measures are required for all spacecraft flying in low earth orbits, and both Japanese and overseas manufacturers of spacecraft materials and spacecraft are showing great expectations for AO protective technology.
KIMOTO concludes by saying as follows: “We were able to show leadership for the establishment of the international standard. Going forward, because of this achievement, I believe more attention will be paid to Japan's technology in the space business.”
It is expected that the new international standard will contribute to promoting space activities in low earth orbits.
Profile

|
|
|---|
All the images are copyrighted ©JAXA unless otherwise noticed.
- Home>
- Global Activity>
- Public Relations>
- JAXA’s>
- JAXA's No.87>
- Developing the International Standard for the Use of AO Protective Technology for Low Earth Orbit Spacecraft