About Infrared Imaging Satellite "AKARI" (ASTRO-F)

|
AKARI: Seeking an understanding of the formation and evolution of galaxiesThe AKARI (ASTRO-F) is Japan’s first infrared-ray astronomical satellite to perform "survey observations," an all-sky surveys of infrared sources, including stars and galaxies. The AKARI was launched on February 22, 2006 (Japan Standard Time, JST) from the Uchinoura Space Center (USC) by the M-V-8 Launch Vehicle.
|
|---|
Project Topics
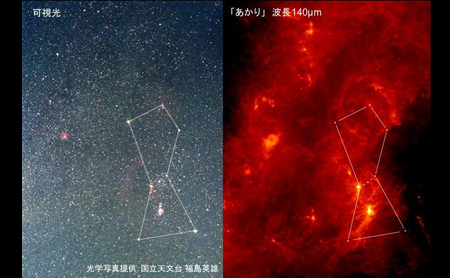
indexHighly detailed data of far-infrared all-sky image

|
A team led by the University of Tokyo compiled a new far-infrared all-sky image using data acquired by the Infrared Astronomical Satellite AKARI. JAXA also cooperated with the team for image data compilation and its publication. The resolution of the compiled data is four to five times better than the previous far-infrared all-sky image, and its observation wave length is also longer. The image data is published on the ISAS site for the use of world researchers. ... |
|---|
Press Release
index-
- Dec. 17, 2018 (14:00) [release]
- Space telescope detects water in a number of asteroids -- Near-Infrared Asteroid Spectroscopic Survey with AKARI --
Characteristics of Infrared Imaging Satellite "AKARI" (ASTRO-F)
Achievements by the onboard infrared observation instruments of AKARI
|
A large portion of infrared light from space does not reach the ground because the Earth’s atmosphere absorbs infrared rays, and, at the same time, emits strong infrared rays. Hence, infrared telescopes have to be lifted above the veiling atmosphere. The AKARI is equipped with a telescope of 68.5-cm caliber. The satellite achieved the extremely high sensitivity by cooling the telescope up to minus 267 degrees Celsius by liquid helium and a cryogenic freezer.
A tremendous amount of data acquired by the AKARI is still useful. In January 2015, the highly detailed far-infrared all-sky image data was released by JAXA/ISAS in cooperation with Japanese universities, including the University of Tokyo, research institutions, and ESA (European Space Agency). |
|
|---|
Major Characteristics
| International Designation Code | 2006-005A |
|---|---|
| Launch Date | 06:28, February 22, 2006 (JST) |
| Launch Vehicle | M-V-8 |
| Location | Uchinoura Space Center |
| Shape | 1.9m x 1.9m x 3.7m 5.5m (at deployment of the solar paddles) |
| Weight | Approx. 952 kg (at launch) |
| Orbiter | Circular (Sun-synchronous polar) |
| Altitude | Approx. 750 km |
| Inclination | 98.4 degrees |
| Period | 100 min |
Contents

- May. 27, 2008
- Approaching the Infinite Mysteries of Space

- Oct. 12, 2006
- Dramatic Birth and Death of Stars
Takao Nakagawa
