About Advanced Earth Observing Satellite "Midori" (ADEOS)
 |
Primary applications include monitoring global environmental changes such as maritime meteorological conditions, atmospheric ozone, and gases that promote global warming. ADEOS was also expected to play a vital role in developing more sophisticated inter-orbit communications and platform technology for the satellite of tomorrow. |
|---|
Observation operation results
|
ADEOS was launched by H-II Launch Vehicle No.4 on August 1996 and provided a large volume of data containing valuable information about our environment atmosphere, ocean and land for about 10 months until it suddenly got out of control on June 30, 1997 because of the structural damage in its solar array paddle. |
|---|
Characteristics of Advanced Earth Observing Satellite "Midori" (ADEOS)
Introducing various sensors.
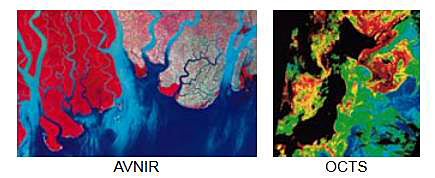
Midori includes the following instrumentation for consolidated continuous measurement of land, sea and air: AVNIR (Advanced Visible Near Infrared Radiometer), OCTS (Ocean Color and Temperature Scanner), both developed by NASDA. In addition, there are six kinds of AO sensors: NSCAT (NASA Scatterometer) and TOMS (Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer), both from NASA, POLDER (Polarization and Directionality of the Earth's Reflectances),a geosurface reflection measuring device from CNES, IMG (Interferometric Monitor for Greenhouse Gases) a sensor for measuring the greenhouse effect from the Ministry of International Trade and Industry, ILAS (Improved Limb Atmospheric Spectrometer), an improved spectrometer for measuring infrared radiation on the edge of the atmosphere, RIS (Retroreflector In-Space), a retroreflector for measuring laser long light-path absorption between the earth and satellites.
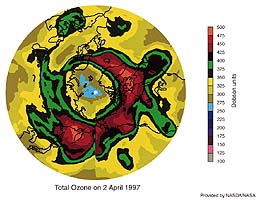
Arctic Ozone Decrease |

A Bird's-Eye View Image Utilizing Stereo AVNIR Images |
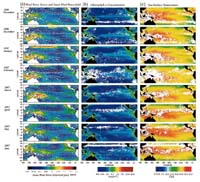
96/97 El Niño Captured by ADEOS |
|---|
Major Specifications
| International Designation Code | 1996-046A |
|---|---|
| Launch Date | 8/17/1996 10:53(JST) |
| Launch Vehicle | H-II Launch Vehicle 4F |
| Launch Site | Tanegashima Space Center |
| Shape | Module type with deployable solar paddle (one wing) Body: Approx. 4×4×5(m) (mission, bus module) Solar Paddle: Approx. 3×26(m) |
| Weight | Approx. 3,560kg |
| Orbit Type | Sun Synchronous Subrecurrent |
| Altitude | Approx 800km |
| Inclination | Approx. 98.6deg |
| Period | Approx. 101min |
| Recurrent Period | 41days |
| Attitude Control | Three-axis stabilized (zero-momentum) |