About H-II Launch Vehicle
 |
The H-II launch vehicle, the central rocket in Japan's space program, with the capability to launch a two-ton class satellite into geostationary orbit, is a two-stage rocket that was developed with Japanese independent technology in all stages. In addition to geostationary satellite, it can also be used to launch payloads into low and medium-altitude orbits. For greater economy, it is possible to launch simultaneously two geostationary satellites weighing about one ton each. |
|---|
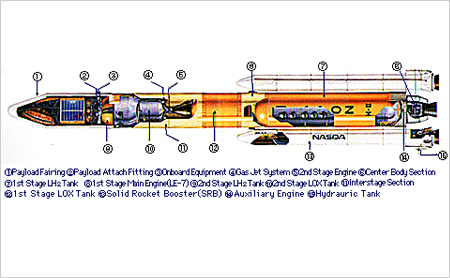
Major characteristics
Configuration
Principal Specifications
|
First Stage
The first stage of the H-II launch vehicle consists of the first stage core vehicle equipped with the LE-7 engine and two solid rocket boosters(SRBs) . The LE-7 engine is a liquid hydrogen/liquid oxygen engine with 86 tons of thrust(at sea level) . The SRBs are polybutadiene composite solid propellant boosters with 158 tons of thrust each(at sea level) . The guidance and control of the first stage is performed by the hydraulically steerable nozzles of the LE-7 engine and of the SRBs controlled by the Inertial Guidance Computer(IGC). Two auxiliary engines are also provided to control attitude.
Second Stage
The second stage of the H-II launch vehicle is equipped with the LE-5A Iiquid hydrogen/liquid oxygen engine. The LE-5A engine is an improved LE-5 engine(developed for the second stage of the H - I launch vehicle) and provides 12 tons of thrust (in vaccum). The guidance and control of the second stage is performed by the hydraulically steerable nozzle of the LE-5A engine and the reaction control system controlled by the IGC.
Guidance and Control System
The H-II launch vehicle employs a strapped-down inertial guidance and control system. The system consists of the Inertial Measurement Unit(lMU) which uses three ring laser gyros and the IGC. The inertial guidance and control system enables the H-Il launch vehicle to correct errors automatically and to maintain the planned orbit without commands from the ground station.
Payload Fairing
The payload fairing protects the payload from the severe launch environment and from contamination on the ground.
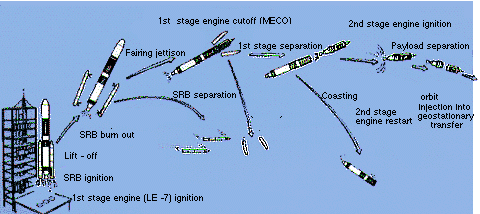
Flight Sequence
Launch Records
| Flight No. | Launch Date | Peyload |
|---|---|---|
| TR-I-1 | 9/6/1988 | The acquisition of the technical data for development of a H-II rocket |
| TR-I-2 | 1/27/1989 | |
| TR-I-3 | 8/20/1989 | |
| 1F | 2/4/1994 | Orbital Re-entry Experiment (OREX) H-II Launch Vehicle Evaluation Payload "Myojo"(VEP) |
| 2F | 8/28/1994 | Engineering Test Satellite VI "KIKU-6"(ETS-VI) |
| 3F | 3/18/1995 | Space Flyer Unit (SFU) Geostationary Meteorological Satellite-5 "Himawari-5"(GMS-5) |
| 4F | 8/17/1996 | Advanced Earth Observing Satellite "Midori"(ADEOS) Japan Amateur Satellite-3 "FUJI-3"(JAS-2) |
| 6F | 11/28/1997 | Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission "TRMM" Engineering Test Satellite VII "KIKU-7"(ETS-VII) |
| 7F | 2/21/1998 | Communications and Broadcasting Engineering Test Satellites "Kakehashi"(COMETS) |
| 8F | 11/15/1999 | Multi-functional Transport Satellite (MTSAT) * Destruct Command was sent as the vehicle went out of the planned flight path. |
 Large Image
Large Image